Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling
DriverMap™ Adaptive Immune Receptor Profiling Assays
Comprehensive and ultra-sensitive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling from any immune sample
Immune Repertoire Profiling is a powerful tool for characterizing adaptive immune responses to cancer, auto-immune and infectious diseases, allergies, vaccinations, and therapeutic treatments. The unique sequences of the T-cell and B-cell receptors (TCRs and BCRs), and antibody variable regions (CDR3) that recognize foreign antigens define the individual differences in adaptive immune responses:
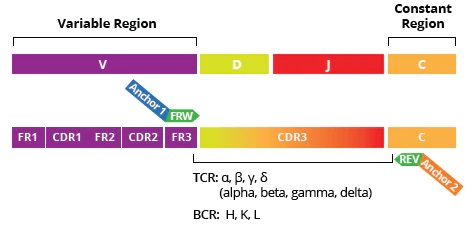 Profiling the TCR and BCR variable regions using Multiplex (RT-)PCR and NGS provides critical data for the discovery of novel, disease-associated immunity biomarkers.
Profiling the TCR and BCR variable regions using Multiplex (RT-)PCR and NGS provides critical data for the discovery of novel, disease-associated immunity biomarkers.
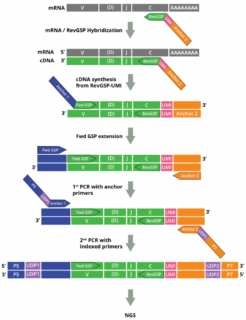
Cellecta’s DriverMap™ AIR assay kit and Immune Repertoire Profiling Services for Human RNA are designed to specifically amplify only functional CDR3 RNA molecules, avoiding non-functional pseudogenes with similar structures. The DriverMap AIR RNA assay quantifies T-cell and B-cell receptor transcripts. Assaying expression of the immune receptors enables highly sensitive detection of low-frequency, rare TCR and BCR clonotypes and comprehensive profiling also when working with small samples and limited numbers of cells. For detailed information about the importance of immune profiling on the RNA level click here
The assay simultaneously amplifies, in a single multiplex RT-PCR reaction, the CDR3 regions of all T-cell receptor (TCR)–TRA, TRB, TRG and TRD–and B-cell receptor (BCR)–IGH, IGK and IKL–chains using a set of 300 experimentally validated RT-PCR primers to yield Illumina-compatible next-generation sequencing (NGS) libraries:
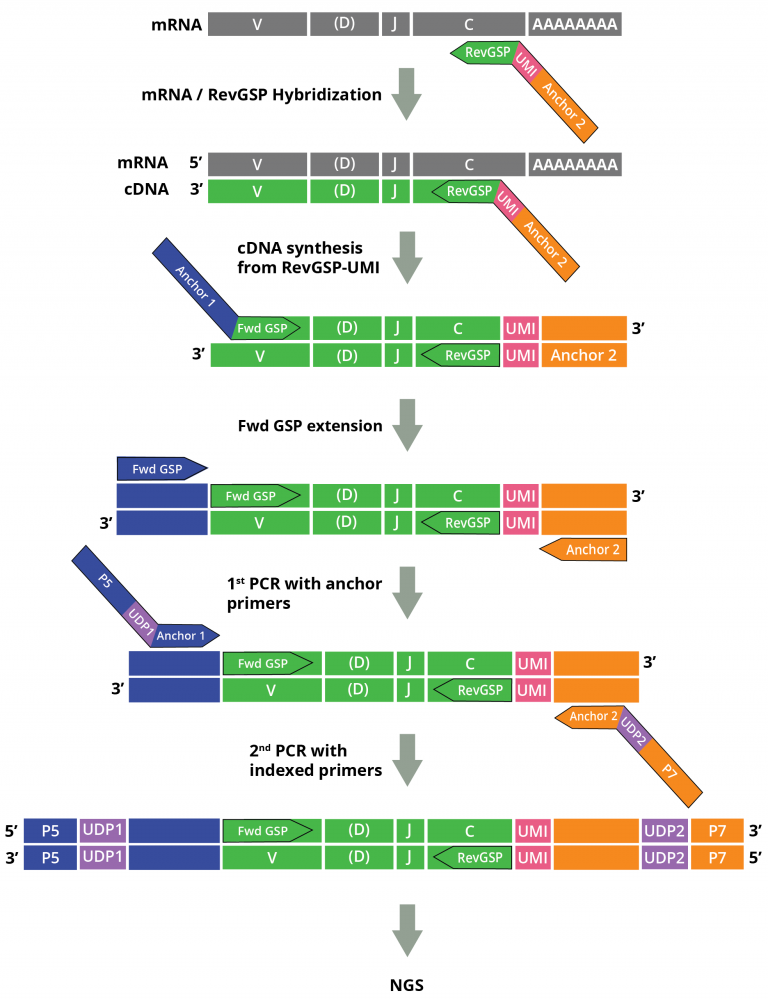
Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling Drivermap AIR RNA Workflow
Synthetic RNA-Spike-In controls as calibration standards for accurate clonotyping can be used in conjunction with the assay.
With DriverMap AIR kits for RNA you get
- The only assay technology on the market that profiles the CDR3 repertoire of all T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) chains in a single-tube assay
- A 3x larger complement of clonotypes than with other assays by using Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs)
- Reproducible and comprehensive coverage from a wide range of sample inputs, including whole blood, PBMCs, dried blood microsamples, FACS-sorted immune cells, cancer biopsies, and tissue samples including FFPE
Optionally, samples used for profiling using the DriverMap AIR kit for Human RNA can also be run, in parallel, through Cellecta´s DriverMap Gene Expression Profiling to obtain phenotypic cell information.
Contact us to receive a quotation for AIR kits or services!
Download the product flyer for a general overview and the AIR technology guide with an introduction to AIR technology and recommendations on designing AIR profiling experiments
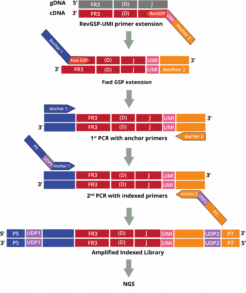
The DriverMap AIR assay for Human DNA amplifies receptor genes directly from genomic DNA:
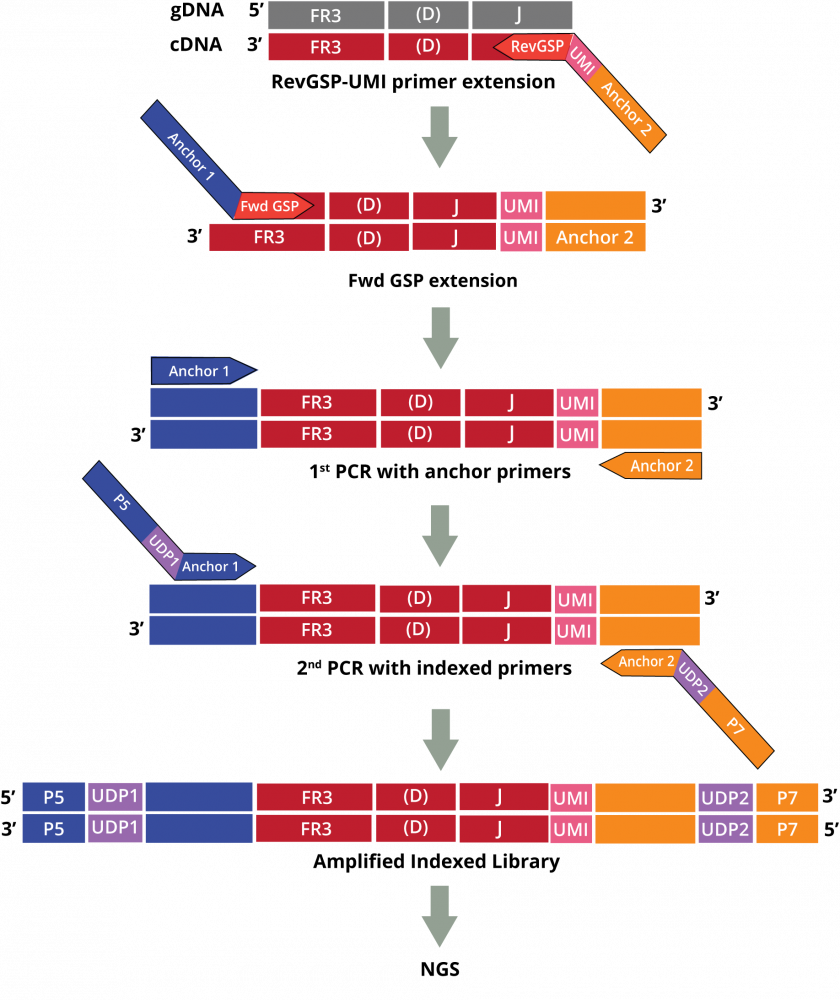
Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling Drivermap AIR DNA Workflow
The AIR DNA assay provides a more quantitative measurement of the genetic copies for each CDR3-specific clonotype which correlates to the number of cells with that clonotype in that sample. This data enables the measurement of clonal expansion in T and B cells.
Combining data obtained from both the AIR DNA and AIR RNA assays enables assessment of both the transcriptional activation and number of cells with a particular clonotype. The ability to differentiate these two effects provides a quantitative basis to assess antigen-activated clonotypes. For example, it is evident from the data in the figure below, that particular TRB clonotypes, even when present in only a small portion of the cells in a population, can be highly up-regulated:
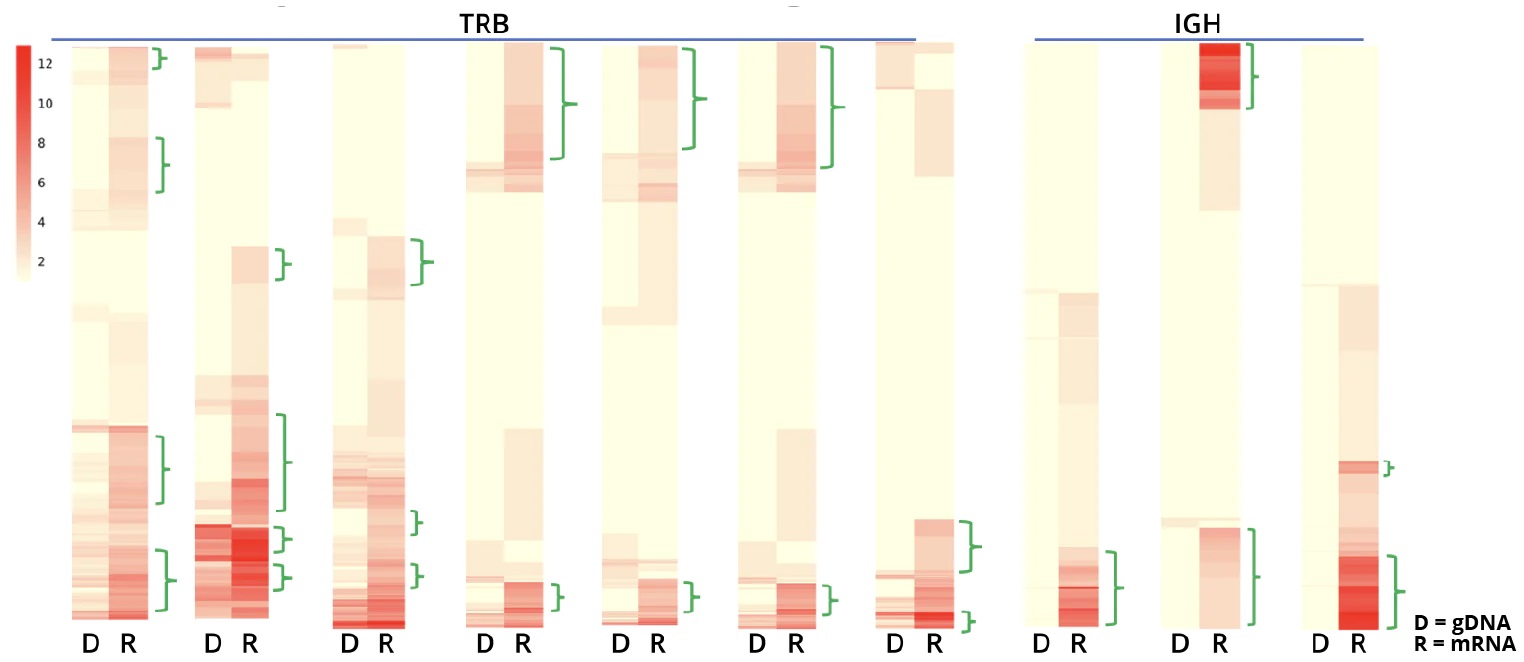
Showing all 10 results