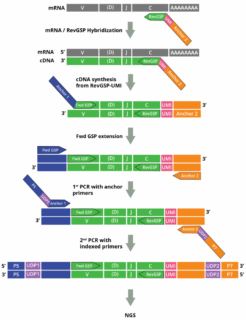
Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling
DriverMap™ Adaptive Immune Receptor Profiling Assays
Comprehensive and ultra-sensitive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling by AIRR-seq from any immune sample
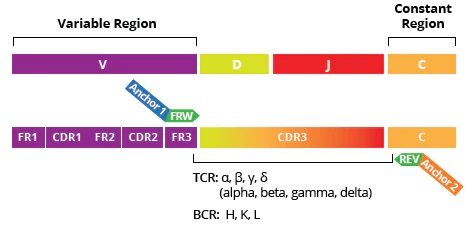
Immune Repertoire Profiling by AIRR-seq is a powerful tool for characterizing adaptive immune responses to cancer, auto-immune and infectious diseases, allergies, vaccinations, and therapeutic treatments. The unique sequences of the T-cell and B-cell receptors (TCRs and BCRs), and antibody variable regions (CDR3) that recognize foreign antigens define the individual differences in adaptive immune responses:
• Multiplex (RT-)PCR and UMI-supported NGS for profiling TCR and BCR variable regions
• Enabling technology for discovery of novel, disease-associated immunity biomarkers
Cellecta’s DriverMap™ AIR assay kit and Immune Repertoire Profiling Services for Human RNA are designed to specifically amplify only functional CDR3 RNA molecules, avoiding non-functional pseudogenes with similar structures. The DriverMap AIR RNA assay quantifies T-cell and B-cell receptor transcripts. Assaying expression of the immune receptors enables highly sensitive detection of low-frequency, rare TCR and BCR clonotypes and comprehensive profiling also when working with small samples and limited numbers of cells. For detailed information about the importance of immune profiling on the RNA level click here
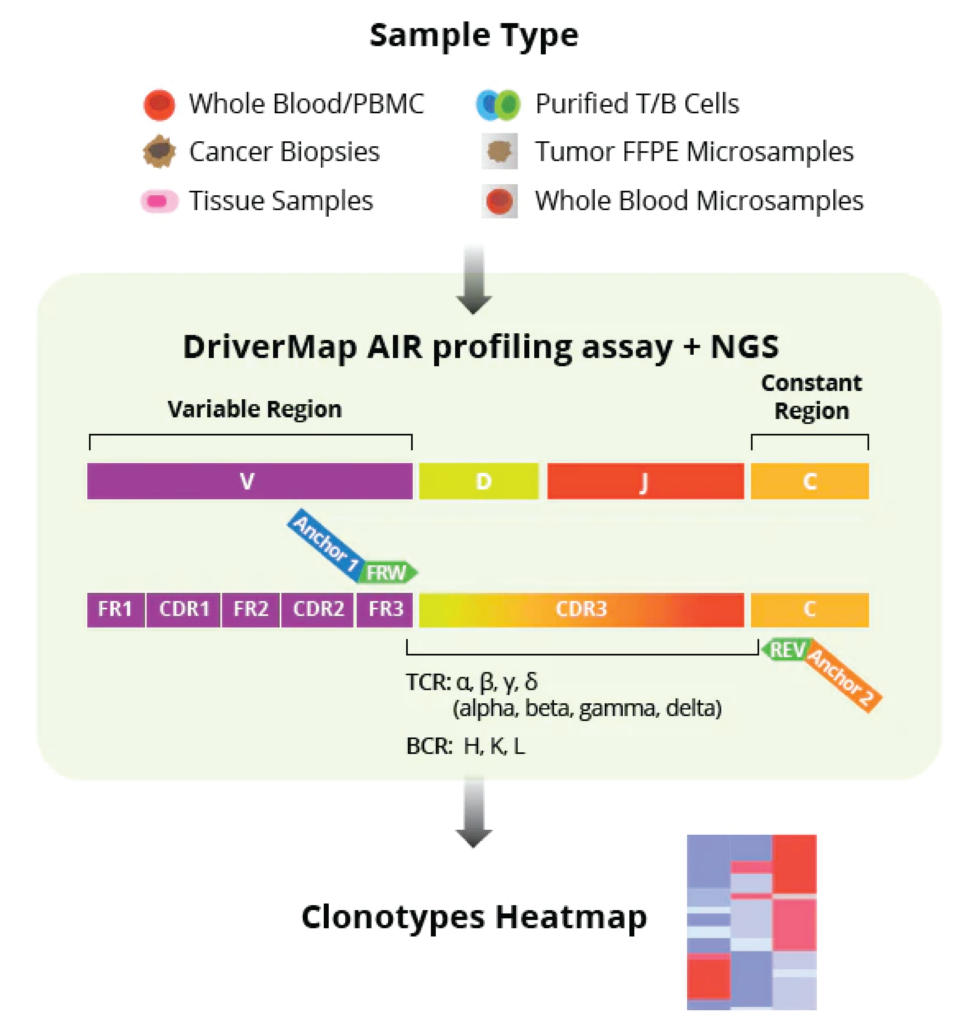
The assay simultaneously amplifies, in a single multiplex RT-PCR reaction, the CDR3 regions of all T-cell receptor (TCR)–TRA, TRB, TRG and TRD–and B-cell receptor (BCR)–IGH, IGK and IKL–chains using a set of 300 experimentally validated RT-PCR primers to yield Illumina-compatible next-generation sequencing (NGS) libraries:
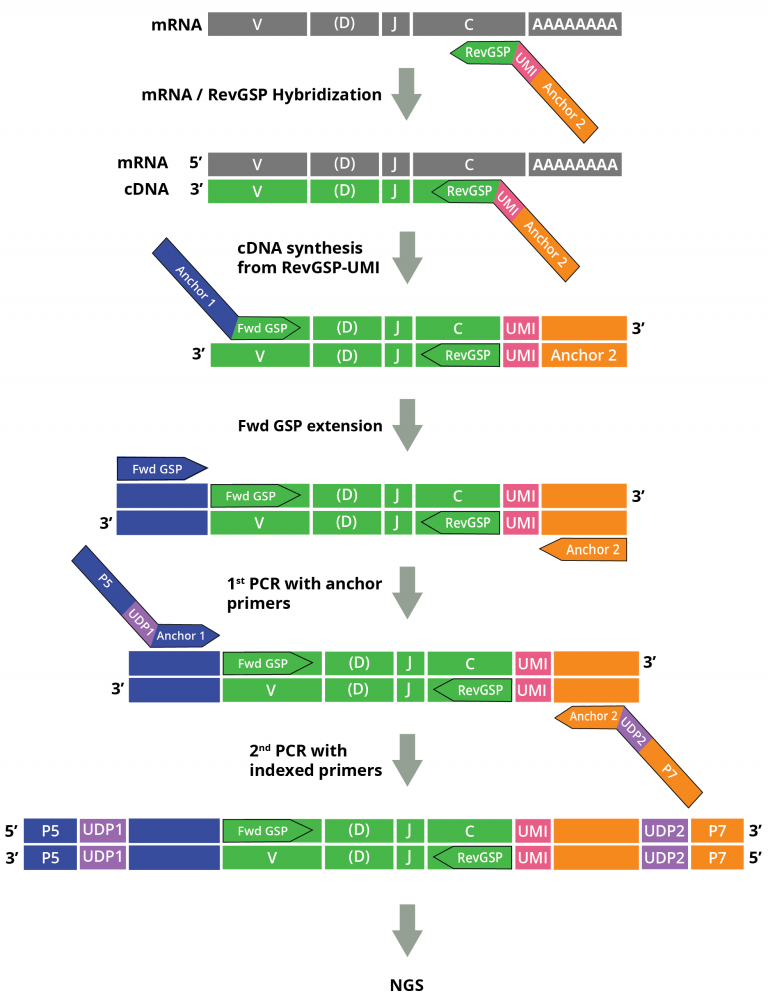
Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling Drivermap AIR RNA Workflow
How is the DriverMap AIR Assay Different from other Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire (AIRR-seq) Assays?
- DriverMap™ Multiplex PCR technology uses gene-specific primers which significantly reduce the level of non-specific binding and primer-dimer amplification products, and are designed to target only TCR/BCR isoforms.
- Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs) facilitate accurate quantitation of the copy number of cDNA or DNA molecules in amplification steps, as well as detection of low abundance clonotypes and correction of amplification biases and sequencing errors.
- Dual-index amplicon labeling strategy minimizes index hopping during NGS allowing for comprehensive readouts.
- Full profiles of the antigen-recognition CDR3 region enable assessment of CDR3 length distribution, V(D)J segment usage, isotype composition for BCRs, somatic mutations, and similar characteristics with immune receptor profiling software such as MiXCR (MiLabs).
Please see the following links for additional resources to learn more about DriverMap AIR technology:
Technology Guide including recommendations on designing AIR profiling experiments
Universal Spike-In RNA Standards for AIRR-Seq
Infographic including kit selection guide
With DriverMap AIR kits for RNA you get
- The only assay technology on the market that profiles the CDR3 repertoire or the full length variable region of all T-cell receptor (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) chains in a single-tube assay
- A 3x larger complement of clonotypes than with other assays by using Unique Molecular Identifiers (UMIs)
- Reproducible and comprehensive coverage from a wide range of sample inputs, including whole blood, PBMCs, dried blood microsamples, FACS-sorted immune cells, cancer biopsies, and tissue samples including FFPE
Optionally, samples used for profiling using the DriverMap AIR kit for Human RNA can also be run, in parallel, through Cellecta´s DriverMap Gene Expression Profiling to obtain phenotypic cell information.
Contact us to receive a quotation for AIR kits or services!
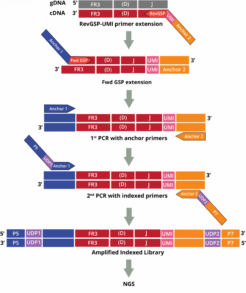
The DriverMap AIR assay for Human DNA amplifies receptor genes directly from genomic DNA:
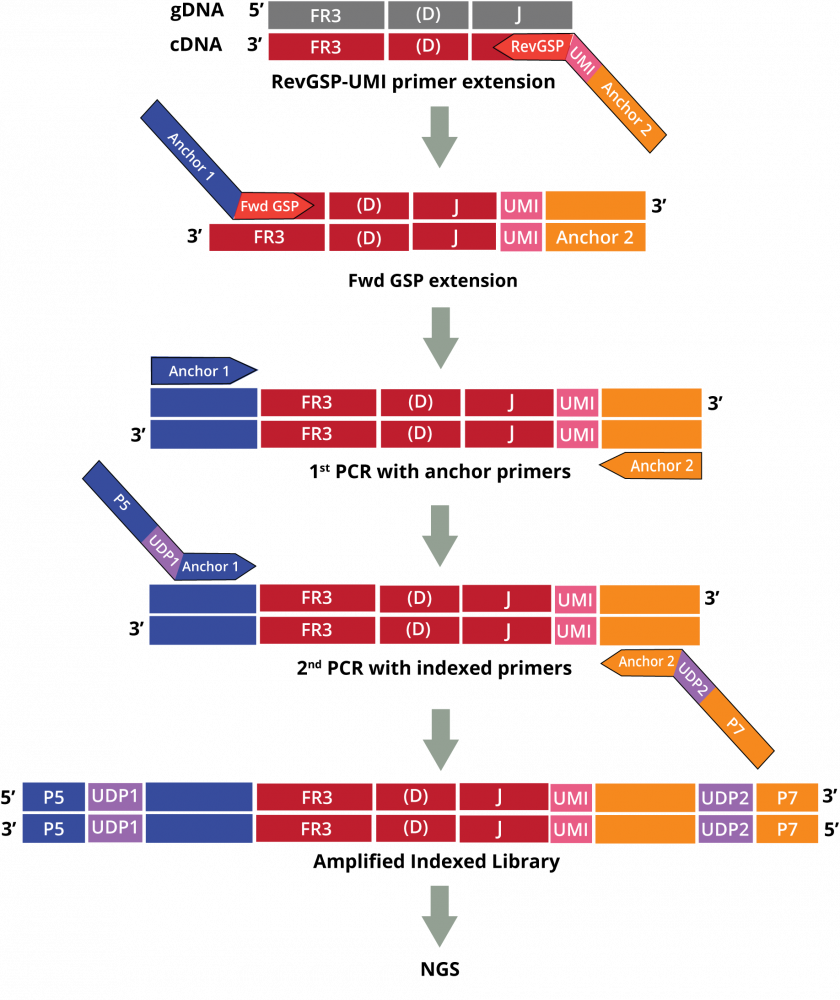
Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling Drivermap AIR DNA Workflow
The AIR DNA assay provides a more quantitative measurement of the genetic copies for each CDR3-specific clonotype which correlates to the number of cells with that clonotype in that sample. This data enables the measurement of clonal expansion in T and B cells.
Combining data obtained from both the AIR DNA and AIR RNA assays enables assessment of both the transcriptional activation and number of cells with a particular clonotype. The ability to differentiate these two effects provides a quantitative basis to assess antigen-activated clonotypes. For example, it is evident from the data in the figure below, that particular TRB clonotypes, even when present in only a small portion of the cells in a population, can be highly up-regulated:
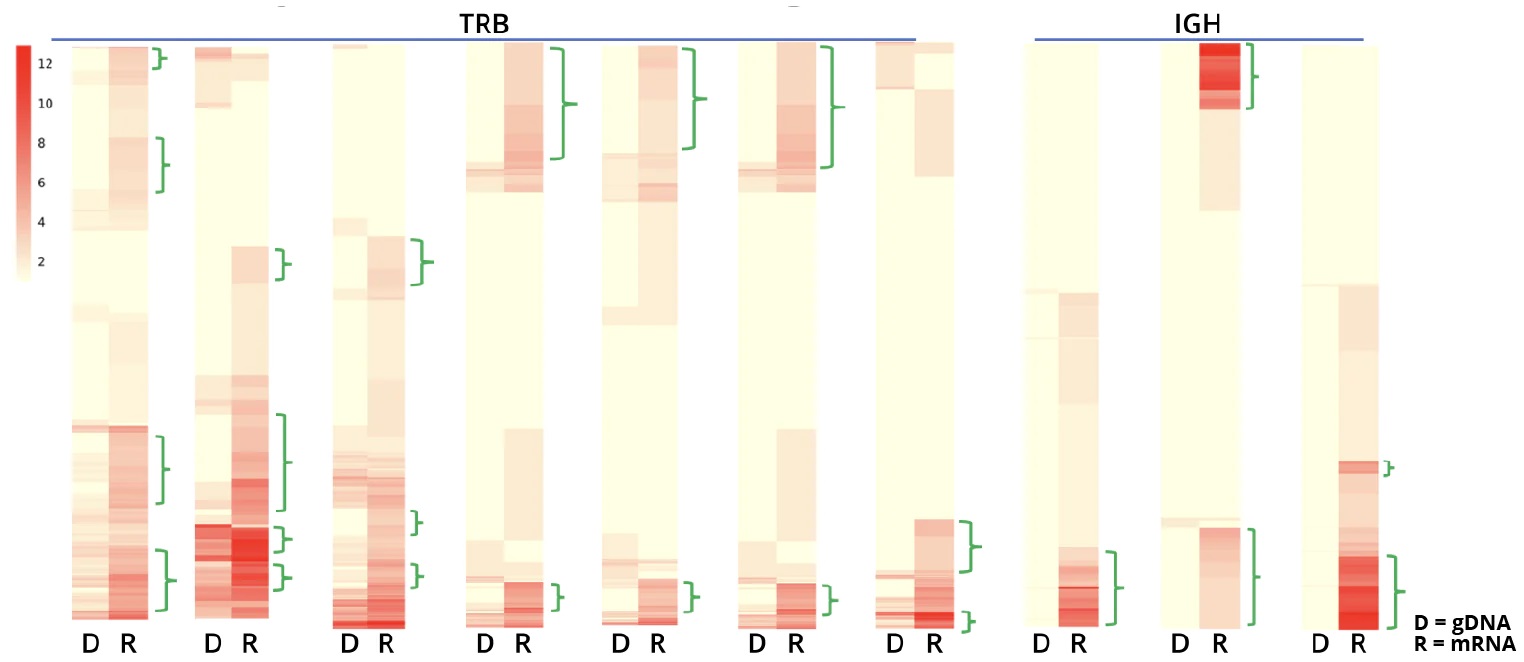
Comparison of CDR3 vs Full-Length Variable Region Repertoire Profiling
The table below summarizes the key differences between profiling only the CDR3 region vs profiling of the full-length variable region.
| DriverMap AIR TCR-BCR (CDR3 only) Profiling | DriverMap AIR TCR-BCR (Full-Length Variable Region) Profiling | |
| Region | CDR3 only | FR1, FR2, FR3, CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3 |
| Amplicon Length (bp) | ~ 300 bp | ~ 600 bp |
| Primer Location |  |
 |
| Starting Material | RNA or DNA | RNA |
| Model System | Human (RNA or DNA)/ Mouse (RNA) | Human |
| NGS Instrument Options | Illumina NextSeq500/550, NextSeq 2000, NovaSeq | Illumina NextSeq 2000 (x 2 300 cycles) kit only |
| How it Works | The CDR3 region determines the structure and specificity of the antigen. The majority of repertoire profiling studies are based on the analysis of only the CDR3 region, as this is the hypervariable region and contains crucial information to study immune repertoire diversity. | The V region encodes CDR1 and CDR2 in germline DNA segments and primarily interacts with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The full-length receptor region is involved in antigen receptor binding affinity and/or downstream signaling and allows one to clone and express the identified and chosen receptors. |
| Key Applications |
|
|
Showing 1–20 of 22 results